Though many smart beta ETFs do provide valuable exposures, others mainly re-shuffle familiar dumb beta factors. Our earlier article showed that traditional, or dumb, Market and Sector Betas account for over 92% of monthly return variance for most U.S. equity smart beta ETFs. This article extends the analysis to international smart beta ETFs.
It turns out that international smart beta ETFs are even more heavily dominated by dumb beta factors than their U.S. counterparts. Consequently, rigorous quantitative analysis is even more critical when deploying smart beta strategies internationally. With capable analytics, investors and allocators can detect unnecessarily complex and expensive re-packaging of dumb international factors as smart beta, identify products that do provide unique exposures, and control for unintended international dumb factor exposures.
Measuring the Influence of Dumb Beta Factors on International Smart Beta ETFs
We started with approximately 800 smart beta ETFs. Since our focus was on the broad international equity strategies, we removed portfolios with over 90% invested in U.S. equities and portfolios dominated by a single sector. We also removed portfolios for which returns estimated from historical positions did not reconcile closely with actual returns. We were left with 125 broad international equity smart beta ETFs, covering all the popular international smart beta strategies.
For each ETF, we estimated monthly positions and then used these positions to calculate portfolio factor exposures to traditional (dumb beta) factors such as global Regions (regional equity markets) and Sectors. These ex-ante dumb factor exposures provided us with replicating portfolios composed solely of traditional dumb beta factors. For each international smart beta ETF, we compared replicating portfolio returns to actual returns over the past 10 years, or over the ETF history, whichever was shorter.
The correlation between replicating dumb factor portfolio returns and actual ETF returns quantifies the influence of dumb beta factors on international smart beta ETFs. The higher a correlation, the more similar an ETF is to a portfolio of traditional, simple, and dumb systematic risk factors.
The Influence of Region Beta on International Smart Beta ETFs
Our simplest test used a single systematic risk factor for each security – Region (Region Market Beta). Region Beta measures exposure to one of 10 broad regional equity markets (e.g., North America, Developing Asia). These are the dumbest traditional international factors and also the cheapest to invest in. Since Market Beta is the dominant factor behind portfolio performance, even a very simple model measuring exposures to regional equity markets with robust statistical techniques delivered 0.95 mean and 0.96 median correlations between replicating dumb factor portfolio returns and actual monthly returns for international smart beta ETFs:
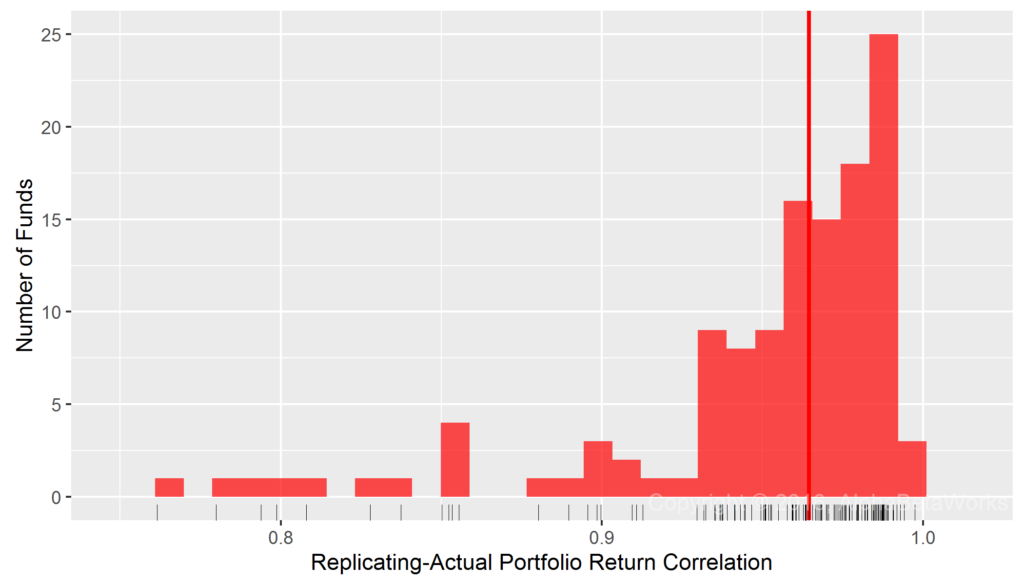
International Smart Beta Equity ETFs: Correlation between replicating Region Factor portfolio returns and actual monthly returns
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 0.6577 0.9390 0.9645 0.9461 0.9818 0.9975
In short: For most broad international smart beta ETFs, Region Market Betas account for at least 93% (0.9645²) of monthly return
The Influence of Region and Sector Betas on International Smart Beta ETFs
We next tested a two-factor model that added Sector Factors. Each security belongs to one of 10 broad sectors (e.g., Energy, Technology). Region and Sector Betas, estimated with robust methods, delivered 0.96 mean and 0.97 median correlations between replicating dumb factor portfolio returns and actual monthly returns for international smart beta ETFs:
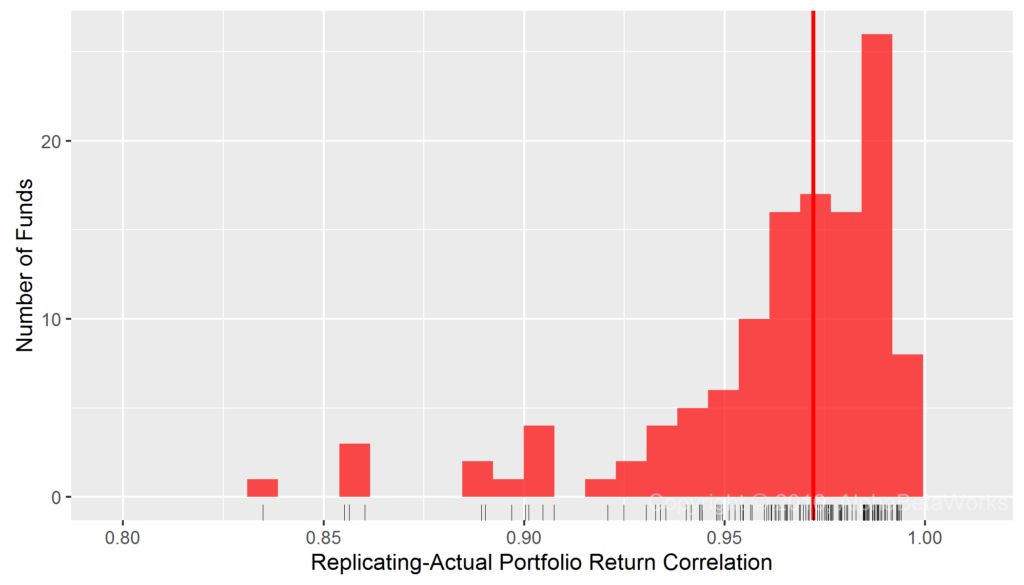
International Smart Beta Equity ETFs: Correlation between replicating Region and Sector Factor portfolio returns and actual monthly returns
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 0.7017 0.9526 0.9722 0.9578 0.9849 0.9941
In short: For most broad international equity smart beta ETFs, Regional Market and Sector Betas account for over 94% (0.9722²) of monthly return variance. Put differently, only less than 6% of the variance is not attributable to simple Region and Sector factors.
International Smart Beta Variance and International Dumb Beta Variance
Rather than measure correlations between replicating dumb beta portfolio returns and actual ETF returns, we can instead measure the fraction of variance unexplained by dumb beta exposures. The Dumb Beta Variance (in red below) is the distribution of ETFs’ variances due to their dumb beta Region and Sector exposures. The Smart Beta Variance (in blue below) is the distribution of ETFs’ variances unrelated to their dumb beta exposures:
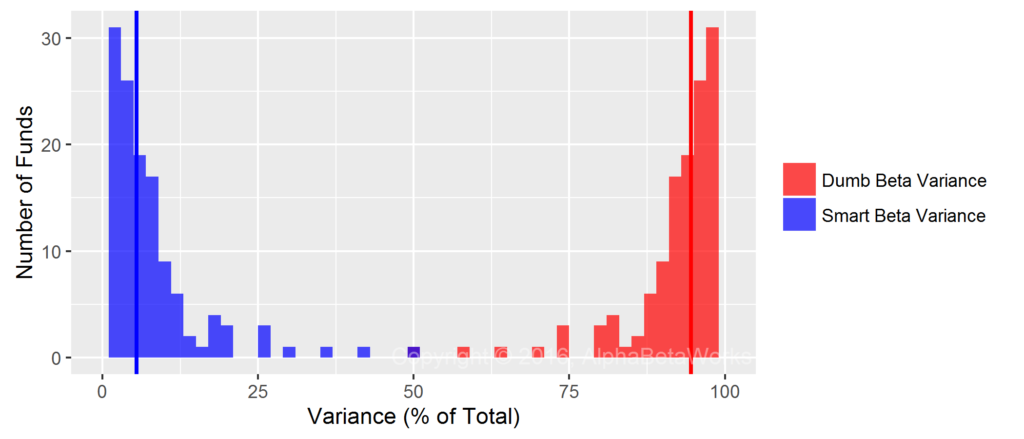
International Equity Smart Beta ETFs: Percentage of variance explained and unexplained by Region and Sector dumb beta exposures
Percentage of international equity smart beta ETFs’ variances due to dumb beta exposures:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 49.24 90.74 94.52 91.95 97.00 98.83
Percentage of international equity smart beta ETFs’ variances unrelated to dumb beta exposures:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. 1.174 3.004 5.484 8.052 9.258 50.760
Note that market timing of dumb beta exposures can generate an active return. This return is still due to traditional dumb factor exposures, but it adds value through smart variation in such exposures. Market timing is a relatively small source of return for most international smart beta ETFs and is beyond the scope of this article.
Our analysis excludes Value/Growth and Size Factors, which are decades old and considered dumb beta by some. If one expands the list of dumb beta factors, smart beta variance shrinks further.
Conclusions
- Traditional, or dumb, Region and Sector Betas account for over 94% of variance for most international smart beta ETFs.
- Smart beta, unexplained by the traditional Region and Sector Betas, accounts for under 6% of variance for most international smart beta ETFs.
- With proper analytics, investors and allocators can guard against elaborate re-packaging of dumb international beta as smart beta and spot the products that actually do provide international smart beta exposures.
- Investors and allocators can monitor and manage unintended dumb factor exposures of international smart beta portfolios.